Match the following term with its correct description basophil – Match the following term with its correct description: basophil. Basophils are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system, particularly in allergic reactions.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of basophils, including their morphology, activation, and clinical significance. By exploring the intricate functions of basophils, we gain a deeper understanding of their involvement in various immune responses.
Basophils: Match The Following Term With Its Correct Description Basophil
Basophils are a type of white blood cell that play a role in the immune system, particularly in allergic reactions.
Define basophil
Basophils are a type of granulocyte, a white blood cell that contains granules in its cytoplasm. They are the least common type of granulocyte, accounting for only about 0.5-1% of circulating white blood cells.
Explain the role of basophils in the immune system
Basophils play a role in the immune system by releasing histamine and other mediators that promote inflammation. Histamine is a chemical that causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, allowing fluid and cells to leak out into the surrounding tissues.
This can lead to swelling, redness, and itching.
Discuss the function of basophils in allergic reactions, Match the following term with its correct description basophil
Basophils are activated by the binding of an allergen to an antibody called IgE. Once activated, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Describe the morphology of basophils
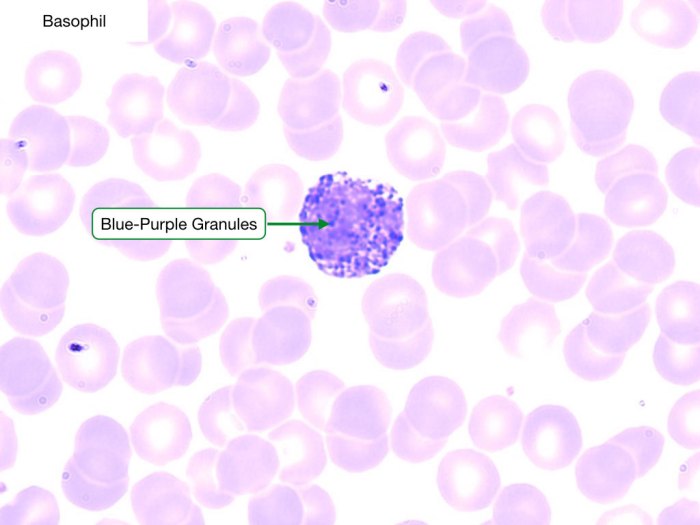
Basophils are typically 10-15 micrometers in diameter and have a bilobed nucleus. The cytoplasm of basophils is filled with large, basophilic granules that contain histamine and other mediators.
Provide details about the size and shape of basophils
Basophils are typically 10-15 micrometers in diameter and have a bilobed nucleus.
Explain the significance of basophil granules
The basophilic granules in basophils contain histamine and other mediators that are released when the basophil is activated.
Discuss the presence of histamine and heparin in basophil granules
Basophils contain large, basophilic granules that contain histamine and heparin. Histamine is a chemical that causes blood vessels to dilate and become more permeable, allowing fluid and cells to leak out into the surrounding tissues. Heparin is a chemical that prevents blood from clotting.
Explain the activation of basophils
Basophils are activated by the binding of an allergen to an antibody called IgE. Once activated, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Describe the stimuli that trigger basophil activation
The binding of an allergen to an antibody called IgE triggers basophil activation.
Discuss the role of IgE and FceRI in basophil activation
IgE is an antibody that binds to allergens. When an allergen binds to IgE, it causes the IgE to cross-link with a receptor on the surface of the basophil called FceRI. This cross-linking triggers the activation of the basophil.
Explain the release of histamine and other mediators from activated basophils
Once activated, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Discuss the clinical significance of basophils
Basophils are associated with allergic diseases, such as asthma and anaphylaxis. In asthma, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the airways to narrow and become inflamed. In anaphylaxis, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and can be life-threatening.
Explain the association between basophils and allergic diseases
Basophils are associated with allergic diseases, such as asthma and anaphylaxis. In asthma, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the airways to narrow and become inflamed. In anaphylaxis, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and can be life-threatening.
Discuss the role of basophils in asthma and anaphylaxis
In asthma, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause the airways to narrow and become inflamed. In anaphylaxis, basophils release histamine and other mediators that cause a sudden drop in blood pressure and can be life-threatening.
Provide examples of basophil-related disorders
Examples of basophil-related disorders include asthma, anaphylaxis, and basophil leukemia.
Expert Answers
What is the primary function of basophils?
Basophils are primarily involved in allergic reactions, where they release histamine and other mediators that trigger inflammation.
What are the characteristic features of basophil granules?
Basophil granules contain histamine and heparin, which are released upon activation and contribute to inflammation and defense mechanisms.
How are basophils activated?
Basophils are activated by stimuli such as allergens, which bind to IgE antibodies on their surface, triggering the release of histamine and other mediators.