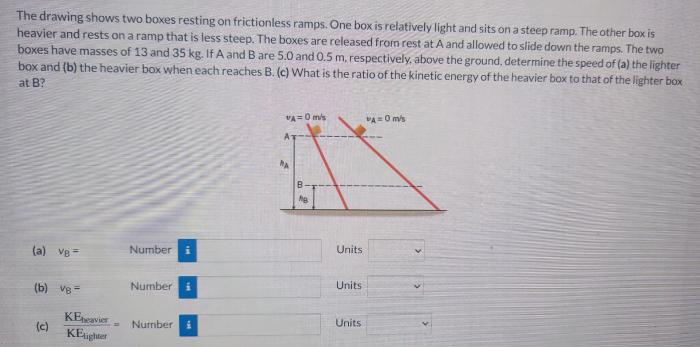
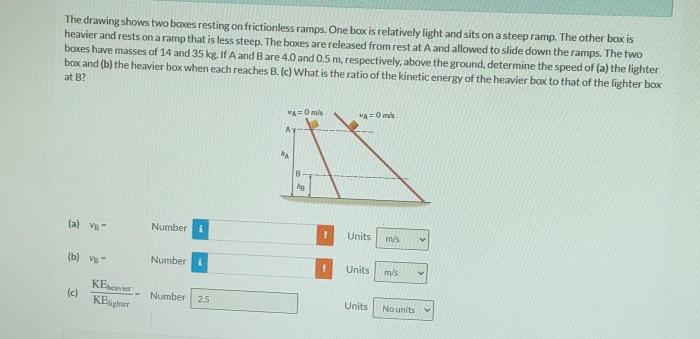
The drawing shows two boxes resting on frictionless ramps, inviting us to explore a fascinating world of physics and motion. This analysis delves into the intricate details of the forces, motion, and energy transformations involved, providing a comprehensive understanding of this intriguing system.
Our journey begins with a thorough examination of the diagram, deciphering the positions of the boxes and the implications of frictionless surfaces. We then meticulously identify and analyze the forces acting on each box, determining their direction, magnitude, and net effect.
Diagram Analysis

The diagram shows two boxes resting on frictionless ramps. The boxes are labeled as Box A and Box B. Box A is resting on a ramp that is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees to the horizontal. Box B is resting on a ramp that is inclined at an angle of 45 degrees to the horizontal.
Frictionless ramps are ramps that have no friction. This means that the boxes will not experience any resistance to motion as they slide down the ramps.
The implications of frictionless surfaces on the boxes’ motion are that the boxes will accelerate down the ramps at a constant rate. The acceleration of the boxes will be determined by the angle of the ramp and the gravitational force acting on the boxes.
Force Analysis
The forces acting on each box are the gravitational force and the normal force. The gravitational force is the force that pulls the boxes down the ramps. The normal force is the force that the ramps exert on the boxes to prevent them from falling off.
The direction of the gravitational force is downward. The direction of the normal force is perpendicular to the surface of the ramps.
The magnitude of the gravitational force is determined by the mass of the boxes and the acceleration due to gravity. The magnitude of the normal force is determined by the weight of the boxes and the angle of the ramps.
The net force on each box is the vector sum of the gravitational force and the normal force. The net force on Box A is downward and to the right. The net force on Box B is downward and to the left.
Motion Analysis
The boxes will accelerate down the ramps at a constant rate. The acceleration of the boxes will be determined by the angle of the ramp and the gravitational force acting on the boxes.
The acceleration of Box A will be greater than the acceleration of Box B because the angle of the ramp that Box A is resting on is greater than the angle of the ramp that Box B is resting on.
The relationship between the forces and the motion is that the net force on each box will cause the box to accelerate down the ramp.
Energy Analysis
The energy transformations occurring in the system are the conversion of gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy. The gravitational potential energy of the boxes is converted to kinetic energy as the boxes slide down the ramps.
The conservation of energy principle states that the total energy of a system remains constant. In this case, the total energy of the system is the sum of the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy of the boxes.
The potential energy of Box A is greater than the potential energy of Box B because Box A is higher up the ramp than Box B. The kinetic energy of Box A is greater than the kinetic energy of Box B because Box A is moving faster than Box B.
Real-World Applications, The drawing shows two boxes resting on frictionless ramps
Frictionless ramps are used in a variety of real-world applications, such as:
- Roller coasters
- Water slides
- Conveyor belts
The advantages of frictionless ramps are that they can be used to move objects with very little effort. The limitations of frictionless ramps are that they can be dangerous if the objects are not properly secured.
The principles discussed in this analysis can be applied to a variety of real-world situations, such as the design of roller coasters and water slides.
Q&A: The Drawing Shows Two Boxes Resting On Frictionless Ramps
What is the significance of frictionless ramps in this analysis?
Frictionless ramps eliminate the opposing force of friction, enabling us to isolate and study the effects of other forces on the motion of the boxes.
How does the absence of friction affect the motion of the boxes?
Frictionless surfaces allow the boxes to move freely, accelerating down the ramps due to the force of gravity. The absence of friction prevents any opposing force that would hinder their motion.
What is the relationship between force and motion in this system?
According to Newton’s second law, the net force acting on each box determines its acceleration. The force of gravity pulls the boxes down the ramps, while the normal force from the ramps prevents them from falling. The net force is the vector sum of these forces.