The tiles below are pieces of a normal ECG, an essential tool for understanding the electrical activity of the heart. This comprehensive guide will provide a step-by-step approach to interpreting these tiles, enabling you to identify the different components, rhythms, and abnormalities that can be detected from an ECG.
By unraveling the secrets hidden within these tiles, you will gain a deeper understanding of the heart’s intricate workings, empowering you to make informed decisions regarding cardiac health.
Components of an ECG: The Tiles Below Are Pieces Of A Normal Ecg
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is composed of three main components: the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
The P wave represents the electrical activity of the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. The QRS complex represents the electrical activity of the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart. The T wave represents the electrical activity of the ventricles repolarizing, or returning to their resting state.
Interpretation of the Tiles
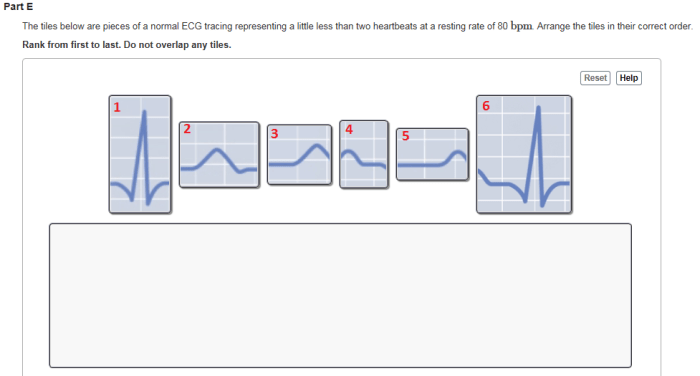
The tiles below are pieces of a normal ECG. To interpret them, we need to identify the different components and their significance.
The first tile shows the P wave. The P wave is a small, positive deflection that occurs before the QRS complex. It represents the electrical activity of the atria.
The second tile shows the QRS complex. The QRS complex is a large, positive deflection that occurs after the P wave. It represents the electrical activity of the ventricles.
The third tile shows the T wave. The T wave is a small, positive deflection that occurs after the QRS complex. It represents the electrical activity of the ventricles repolarizing.
Rhythm Analysis
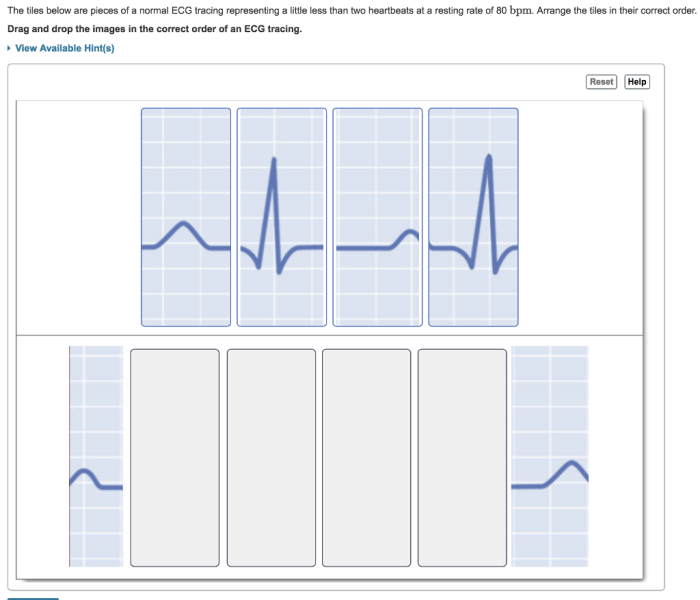
The rhythm of an ECG can be determined by measuring the time between the QRS complexes. The normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. A heart rate that is too fast is called tachycardia, while a heart rate that is too slow is called bradycardia.
The rhythm of an ECG can also be regular or irregular. A regular rhythm is one in which the time between the QRS complexes is constant. An irregular rhythm is one in which the time between the QRS complexes varies.
Axis Determination
The electrical axis of an ECG is a measure of the direction of the electrical activity of the heart. The normal electrical axis is between -30 and +90 degrees. An electrical axis that is too far to the left is called left axis deviation, while an electrical axis that is too far to the right is called right axis deviation.
The electrical axis can be determined by measuring the amplitude of the QRS complex in the different leads of an ECG. The lead with the highest amplitude QRS complex is called the positive pole, while the lead with the lowest amplitude QRS complex is called the negative pole.
The electrical axis is then determined by drawing a line between the positive and negative poles.
Chamber Enlargement and Hypertrophy
Chamber enlargement and hypertrophy can be identified on an ECG by measuring the size of the different waves and complexes. Chamber enlargement is a condition in which the chambers of the heart are enlarged, while hypertrophy is a condition in which the walls of the heart are thickened.
Chamber enlargement and hypertrophy can be caused by a variety of conditions, including hypertension, heart disease, and cardiomyopathy. The ECG changes associated with chamber enlargement and hypertrophy can help to diagnose these conditions.
Ischemia and Infarction
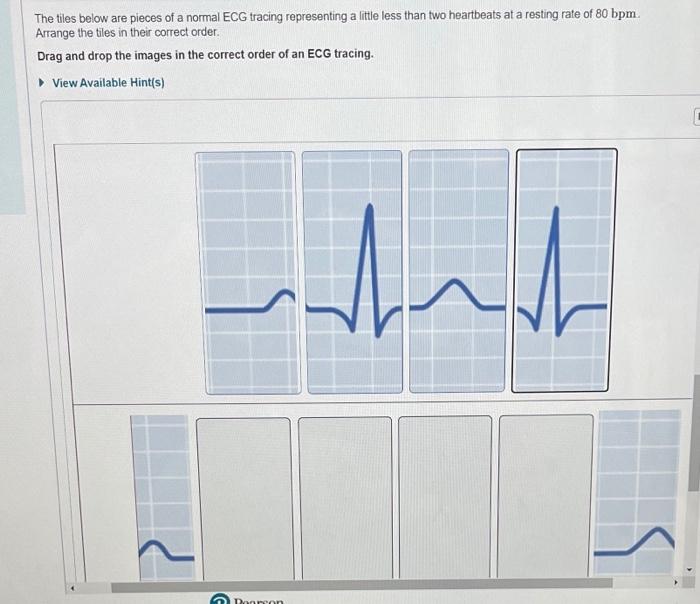
Ischemia is a condition in which the blood supply to the heart is reduced. Infarction is a condition in which the blood supply to the heart is completely blocked. Ischemia and infarction can cause ECG changes that can help to diagnose these conditions.
The ECG changes associated with ischemia and infarction include ST segment depression, ST segment elevation, and T wave inversion. ST segment depression is a condition in which the ST segment is below the baseline. ST segment elevation is a condition in which the ST segment is above the baseline.
T wave inversion is a condition in which the T wave is upside down.
Arrhythmias
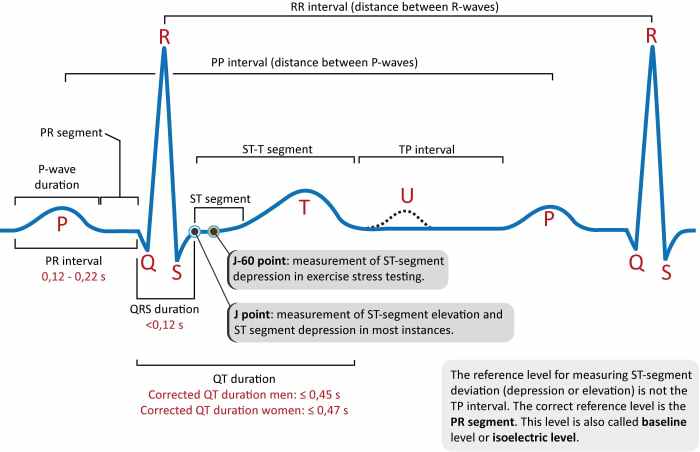
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms. Arrhythmias can be caused by a variety of conditions, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and medications. Arrhythmias can be classified as either supraventricular arrhythmias or ventricular arrhythmias.
Supraventricular arrhythmias are arrhythmias that originate in the atria or atrioventricular node. Ventricular arrhythmias are arrhythmias that originate in the ventricles. Arrhythmias can be either benign or life-threatening. The ECG changes associated with arrhythmias can help to diagnose and classify these conditions.
User Queries
What is an ECG?
An ECG (electrocardiogram) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart over time.
What are the different components of an ECG?
The main components of an ECG include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, each representing specific electrical events in the heart.
How can I interpret an ECG?
ECG interpretation involves identifying the different components and their relationships to determine the heart rate, rhythm, and any potential abnormalities.