Smith Nephew meniscal root repair has emerged as a cutting-edge surgical technique that offers a promising solution for preserving knee function. This article delves into the intricacies of this procedure, exploring its surgical techniques, patient selection, postoperative care, and potential outcomes.
Meniscal Root Repair: Smith Nephew Meniscal Root Repair
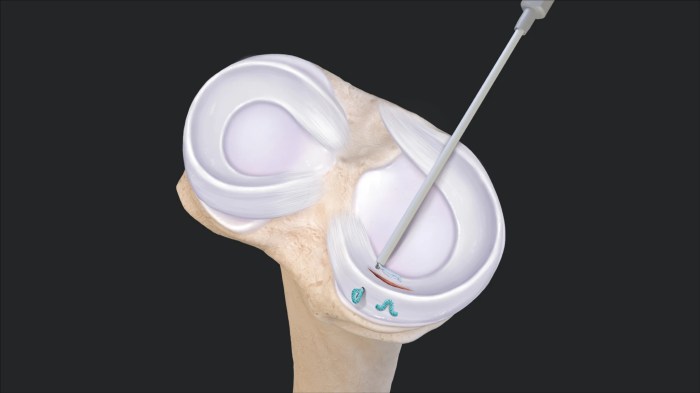
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that sits between the shinbone (tibia) and thighbone (femur) in the knee. It acts as a shock absorber and helps to stabilize the joint. A meniscal root tear is a tear that occurs at the point where the meniscus attaches to the tibia or femur.
These tears can be caused by a sudden twisting or turning motion of the knee, or by repeated stress over time.
Meniscal root tears can be a serious problem because they can lead to pain, swelling, and instability of the knee. They can also increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Meniscal root repair is a surgical procedure that can be used to repair these tears and restore the function of the knee.
Surgical Techniques
There are a number of different surgical techniques that can be used to repair meniscal root tears. The most common technique is open repair, which involves making an incision over the knee and directly repairing the tear. Other techniques include arthroscopic repair, which is performed through small incisions using a camera and specialized instruments, and all-inside repair, which is performed entirely within the knee joint.
Patient Selection and Preoperative Planning, Smith nephew meniscal root repair
The decision of whether or not to undergo meniscal root repair is based on a number of factors, including the severity of the tear, the patient’s age and activity level, and the presence of any other knee problems. Preoperative imaging, such as an MRI, is used to confirm the diagnosis and to plan the surgical approach.
Surgical Procedure
The surgical procedure for meniscal root repair typically takes about 1-2 hours. The patient is positioned lying on their back, and a tourniquet is placed around the thigh to control bleeding. The surgeon then makes an incision over the knee and exposes the meniscus.
The torn root is then prepared for repair by removing any damaged tissue and creating a smooth surface for the suture to attach to.
The surgeon then places sutures through the torn root and anchors them to the bone. The sutures are tied down, and the incision is closed. The patient is typically able to go home the same day as surgery.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
After surgery, the patient will need to follow a rehabilitation program to help the meniscus heal and to restore the function of the knee. The rehabilitation program typically includes:
- Pain management
- Wound care
- Physical therapy
The patient will typically need to wear a brace for 4-6 weeks after surgery to protect the meniscus while it heals. Physical therapy will help the patient to regain range of motion and strength in the knee.
Outcomes and Complications
The success rate of meniscal root repair is high. Most patients experience significant improvement in pain and function after surgery. However, there are some potential complications that can occur, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve damage
These complications are rare, but they can be serious. If you experience any of these symptoms after surgery, it is important to see your doctor right away.
Future Directions
There is ongoing research to improve the techniques and outcomes of meniscal root repair. One area of research is the development of new suture materials and fixation devices that are stronger and more durable. Another area of research is the development of new surgical techniques that are less invasive and have a faster recovery time.
Detailed FAQs
What is the success rate of Smith Nephew meniscal root repair?
Studies have reported success rates ranging from 70% to 90%, with high patient satisfaction and improved knee function.
What are the potential complications of Smith Nephew meniscal root repair?
Potential complications include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and failure of the repair.
How long is the recovery time after Smith Nephew meniscal root repair?
Recovery typically takes several months, involving a gradual return to activity and physical therapy to regain knee function.
