Dive into the fascinating world of cell division with our comprehensive cell division gizmos answer key. This guide unravels the complexities of mitosis and meiosis, providing a clear understanding of the fundamental processes that govern cell reproduction.
The interactive Gizmo simulation empowers you to explore the intricate stages of cell division, making learning both engaging and interactive. Discover the benefits and limitations of simulations in science education, and delve into real-world applications that showcase the practical significance of cell division in fields like medicine and biotechnology.
Cell Division Overview
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It is essential for growth, development, and repair of organisms. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
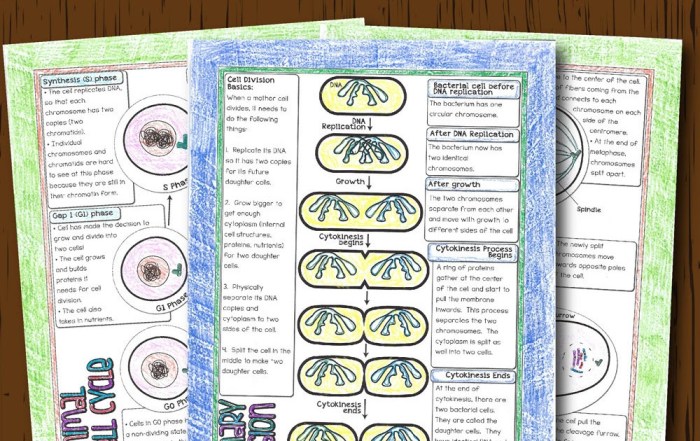
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is used for growth and repair of tissues. Mitosis occurs in four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four haploid daughter cells. It is used for the production of gametes (eggs and sperm). Meiosis occurs in two stages: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Stages of Mitosis, Cell division gizmos answer key
- Prophase:Chromosomes condense and become visible. The nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase:Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes. The cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis
- Meiosis I:
- Prophase I:Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over.
- Metaphase I:Homologous chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase I:Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, resulting in two haploid daughter cells.
- Meiosis II:
- Prophase II:Chromosomes condense and become visible.
- Metaphase II:Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell.
- Anaphase II:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
Visual Representation of Cell Division
[Insert visual representation of cell division here]
Gizmo Simulation
The “Cell Division Gizmo” is an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the process of cell division. The simulation includes a variety of features that allow students to control the conditions of the simulation and observe the results.
Students can use the simulation to explore the different stages of cell division, including mitosis and meiosis. They can also explore the effects of different factors on cell division, such as the presence of toxins or mutations.
Using the Simulation
To use the simulation, students first select the type of cell division they want to explore. They can then set the conditions of the simulation, such as the temperature, the presence of toxins, or the type of mutation.
Once the simulation is running, students can observe the process of cell division in real time. They can zoom in and out of the cell to see the details of the process. They can also pause the simulation at any time to take measurements or to answer questions.
Benefits of Simulations
Simulations can be a valuable tool for science education. They allow students to explore complex concepts in a safe and controlled environment. Simulations can also help students to visualize abstract concepts and to develop their critical thinking skills.
Limitations of Simulations
While simulations can be a valuable tool for science education, they also have some limitations. Simulations are not always realistic, and they may not always accurately represent the real world. Additionally, simulations can be time-consuming to create and to use.
Answer Key Analysis
The Gizmo simulation questions assess students’ understanding of the key concepts of cell division. The answers to the questions are as follows:
1. How many chromosomes are in a normal human body cell?
A normal human body cell contains 46 chromosomes.
2. What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells, while meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
3. What is the role of the spindle fibers in cell division?
The spindle fibers are responsible for separating the chromosomes during cell division.
4. What is the significance of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a repeating series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. It is essential for the proper growth and development of organisms.
5. What are the different stages of the cell cycle?
The different stages of the cell cycle are: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
6. What are the checkpoints in the cell cycle?
The checkpoints in the cell cycle are points at which the cell checks for errors before proceeding to the next stage.
Hey there, I was looking for the cell division gizmos answer key and came across an interesting article about a lab experiment involving a block weighing 80 N ( in a lab a block weighing 80 n ). It’s not directly related to cell division, but it’s a cool example of how physics principles are applied in real-world settings.
Anyway, back to the cell division gizmos answer key…
7. What are the consequences of errors in cell division?
Errors in cell division can lead to a variety of problems, including cancer and birth defects.
Interactive Exercises: Cell Division Gizmos Answer Key
Interactive exercises are essential for reinforcing the concepts of cell division. These exercises provide students with opportunities to apply their knowledge in new situations and receive feedback on their understanding.
Interactive exercises can take a variety of forms, such as:
- Multiple-choice questions
- Drag-and-drop activities
- Simulations
- Case studies
When designing interactive exercises, it is important to keep the following in mind:
- The exercises should be aligned with the learning objectives.
- The exercises should be challenging but not overly difficult.
- The exercises should provide feedback to students on their performance.
Interactive exercises can be a valuable tool for helping students learn about cell division. By providing students with opportunities to apply their knowledge and receive feedback, interactive exercises can help students develop a deeper understanding of this important topic.
Real-World Applications
Cell division is a fundamental process that drives growth, development, and reproduction in all living organisms. Understanding cell division has far-reaching implications in various fields, including medicine and biotechnology.
In medicine, cell division is crucial for tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cells, which have the ability to divide and differentiate into specialized cell types, are used in regenerative medicine to treat conditions such as burns, heart disease, and spinal cord injuries.
Cancer Treatment
- Cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell division. Understanding cell division is essential for developing effective cancer treatments. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy target rapidly dividing cancer cells to inhibit their growth.
- Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This approach relies on an understanding of cell division and the immune response.
Biotechnology
- Cell division is essential for the production of biopharmaceuticals, such as vaccines, antibodies, and enzymes. Biotechnology companies use cell culture techniques to grow and divide cells to produce these therapeutic agents.
- Genetic engineering involves modifying the genetic material of cells to create desired traits. This technique relies on cell division to propagate the modified cells and produce organisms with the desired characteristics.
Research
- Studying cell division provides insights into fundamental biological processes, such as growth, development, and aging. Researchers use cell division models to investigate the molecular mechanisms that control these processes.
- Understanding cell division is also crucial for studying cell differentiation, stem cell biology, and tissue engineering.
Question Bank
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis produces four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
How can I use the Gizmo simulation to study cell division?
The Gizmo simulation allows you to visualize and manipulate the stages of cell division, experiment with different variables, and test your understanding through interactive exercises.
What are the practical applications of cell division?
Cell division plays a crucial role in growth, repair, reproduction, and genetic diversity. It is essential for the development of multicellular organisms and has applications in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and cancer research.